What does a VPN concentrator do?
In the modern digital landscape, where remote work has become the norm and online security is paramount, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as essential tools for protecting network communications. VPN concentrators, a vital component within the realm of VPNs, play a pivotal role in enhancing secure connections and remote access. But what exactly does a VPN concentrator do, and how can it benefit your organization?
Let’s delve into the world of VPN concentrators, explore their benefits and costs, examine different types, and decide on the best VPN protocol for your needs. Additionally, we’ll discuss the importance of maintaining robust security within your network.
VPN Concentrator Benefits and Costs:

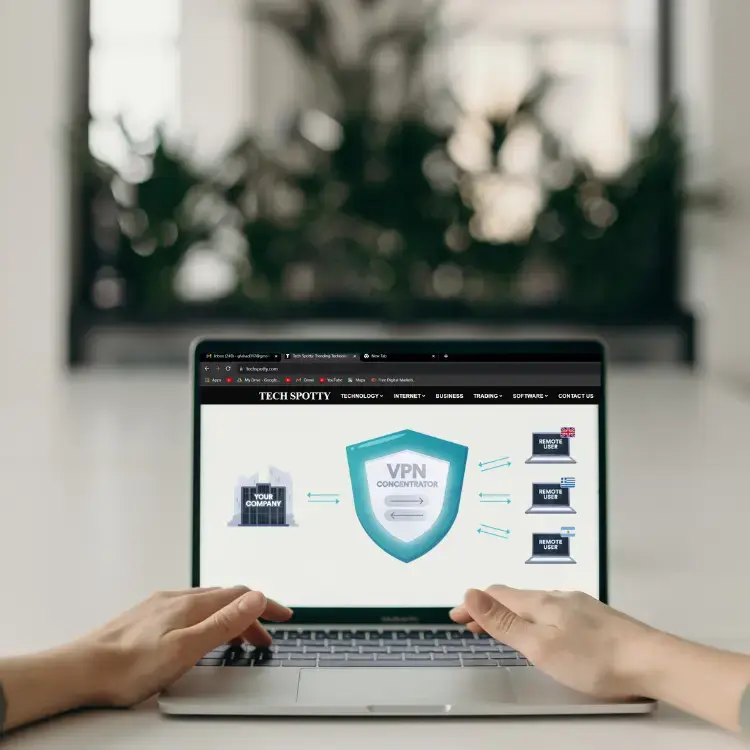
VPN concentrators, often positioned at the corporate network’s edge, are guardians of secure communication between various remote networks, clients, and the central corporate network. Their primary purpose is to extend the protective security boundary of the corporate network out to remote branches or individual devices like workstations, tablets, phones, and even IoT devices.
The core functions of VPN concentrators involve key negotiation, authentication, encryption, and decryption. Encryption can occur in two modes: transport mode, which encrypts only the data payload while preserving the original packet headers, and tunnel mode, which encrypts the entire packet and encapsulates it in a new IP datagram. Choosing between these modes is a crucial consideration when designing your VPN security.
When selecting a concentrator, various factors influence your decision. Your network’s design specifics, such as network address translation and vendor recommendations, will guide you in choosing the correct topology. Smaller models might be software-based, while larger ones could incorporate dedicated hardware for encryption and decryption, capable of supporting thousands of VPN tunnels. Redundancy, load balancing, and other requirements will also influence your choice.
For organizations with budget constraints and multiple remote offices, open-source options like OpenVPN, pfSense, native Linux implementations, and VyOS offer cost-effective alternatives for creating custom VPN concentrators.
Also Read Why Does My iPhone’s VPN Keep Turning On?
Types of VPN Concentrators:
VPN concentrators come in different shapes and sizes, catering to various organizational needs. These types include hardware-based appliances, software-based virtual machines (VMs), container implementations, and even open-source solutions.

Hardware-Based Appliances: These are dedicated devices designed explicitly for VPN concentration. They are often sized for a specified number of VPN connections and offer robust performance.
Software-Based VMs and Containers: Smaller-scale VPN concentrators can be implemented as software-based VMs or containerized solutions. These are more flexible and can be easily deployed and scaled as needed.
Open-Source Solutions: Organizations with tight budgets and technical know-how can explore open-source projects like OpenVPN, pfSense, native Linux implementations, and VyOS. These solutions offer customization options but may require more hands-on management.
Also Read VPN Showdown: A Comprehensive Comparison of the Best Providers
Which VPN protocol is best?

Regarding VPN protocols, two primary contenders dominate the field: IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) and Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS). Each has its advantages and is suited to different use cases.
IPsec: IPsec relies on operating system extensions to create VPN tunnels. Due to its robust security features, it is frequently the preferred option for linking networks between branches and corporate networks.
SSL/TLS: SSL/TLS is integrated into web browsers, making it more widely available across various devices. It is commonly used for connecting individual hosts to corporate networks.
Choosing the proper protocol entails understanding the differences in speed, security risks, and technology. It’s crucial to avoid the security pitfalls of split tunnelling, ensuring comprehensive protection.
Also Read How Do You Mirror to a Smart TV When Using a VPN?
Maintaining Good Security:
Network security cannot function without VPNs, including VPN concentrators, but they are only one element of the picture. In a time when cyber dangers are constantly evolving, maintaining strong security calls for a comprehensive strategy.
Periodic reviews of your organization’s security systems are essential. New security threats like malware and data breaches pose significant risks, including credit card theft and intellectual property disclosure. Diligence is the key to safeguarding your critical assets.
Bottom Line:
In a world where remote work is rising, VPN concentrators are guardians of secure communication. Understanding their role, choosing the right type and protocol, and maintaining overall network security are essential to ensuring a resilient and protected digital infrastructure.
10 Useful and Unique FAQs with Answers
What is a VPN concentrator, and how does it differ from a VPN router?
A VPN concentrator is designed to manage and secure multiple VPN connections, making it ideal for organizations with numerous remote branches or clients. In contrast, a VPN router primarily routes traffic and may support VPN functionality on a smaller scale.
Can I use a VPN concentrator for personal use, or is it mainly for businesses?
While VPN concentrators are frequently used by companies to safeguard their networks, they can also be advantageous to people looking for improved security for their remote connections, particularly if they have many devices.
What are the key security features to look for in a VPN concentrator?
Key security features include robust encryption methods, authentication protocols, support for multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection/prevention, and regular software updates.
How can I ensure the scalability of my VPN concentrator as my organization grows?
To ensure scalability, choose a VPN concentrator that supports additional VPN tunnels and consider redundancy and load-balancing configurations.
What are the advantages of open-source VPN concentrator solutions?
Open-source solutions are cost-effective and offer customization options. However, they may require more technical expertise for setup and management.
Is split tunnelling a good idea when using a VPN concentrator?
Split tunnelling should be used cautiously, as it can introduce security risks by allowing some traffic to bypass the VPN. Additional security measures should be implemented if split tunnelling is necessary.
Are there any legal considerations when deploying a VPN concentrator, especially in international settings?
Yes, deploying a VPN concentrator can have legal implications, especially when crossing international boundaries. Ensure compliance with local data protection and privacy laws.
Can a VPN concentrator help with improving network performance?
While VPN concentrators primarily focus on security, they can indirectly enhance network performance by efficiently managing VPN connections and reducing latency.
What is the role of Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) in VPN concentrators?
DMVPN is a mechanism that simplifies the configuration of many site-to-site IPsec VPNs, making it easier to manage multiple VPN connections efficiently.
How often should I review my organization’s network security, including the VPN concentrator setup?
Regular security reviews are essential. Aim for at least an annual assessment, but more frequent checks may be necessary