Intel 13th Generation Processors – Is It Worth The Upgrade?
Are you considering upgrading to Intel’s 13th Generation Processors?
With an improved design and increased performance, these CPUs offer a tempting option for tech enthusiasts looking to keep up with the latest technological advancements.
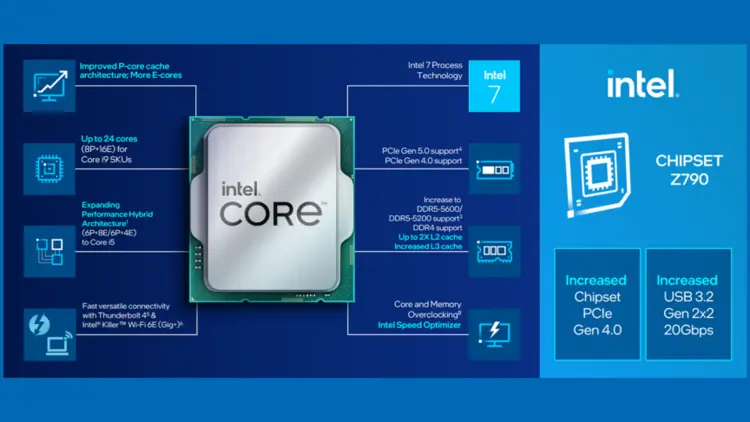
Understanding The Intel 13th Generation Processors
The 13th Generation Processors from Intel feature multiple advancements such as improved performance, enhanced graphics capabilities, and greater efficiency.
Overview Of The Latest Processor Technology
The technology behind Intel’s 13th-generation processors is an improved version of the Raptor Lake microarchitecture CPUs.
The new iterations of these CPUs come with support for newer technologies such as DDR5 RAMs and PCIe 5.0 storage devices, allowing for faster data transfer between components.
So how much of an improvement are we talking about?
According to a case study, 13th gen processors have improved single and multi-threaded benchmarks, Intel’s best 13th Gen processor (i9 13900KS) was benchmarked at 10% higher than its counterpart – the 12th Generation (i9 12900KS).

So, to generalize: Every processor core sees a 10-15% increase in single-threaded performance compared to its predecessor, giving more tasks greater speed gains when running on a single core. Multithreaded performance can experience up to 41% jump due to the larger cache memory (up to 36 MB L3 cache).
Overall, users should expect much better gaming performance along with significantly reduced power consumption from their systems after upgrading to this latest generation of Intel processors – making them well worth considering if concerned about system efficiency or raw computing power needs that only an integrated CPU platform can provide.
Key Differences From Previous Generations
Enhanced graphics capabilities are also included in the chip with hardware support for visuals like Dolby Vision HDR.
The Thread Director Technology in Intel’s processors is responsible for efficient power consumption and better allocation of workloads on appropriate cores, leading to exceptional battery life without killing performance numbers.
Also Check: Dual Core i7 vs Quad Core i7 Macbook Pro – Detailed Comparison
Additionally, these CPUs are compatible with 600-series motherboards which offer 8x PCI Express lanes for peripheral connectivity but offer 20 lanes when updated to 13th Gen drivers – allowing faster read/write times compared to their predecessors alongside great upgrade affordability since they don’t require replacing any existing components except maybe the CPU itself.
Intel’s latest CPU series provides significant boosts over AMD Ryzen in terms of raw performance figures, easily justifying its higher price tag while offering incremental improvements compared to supporting chipsets from 11th and 12th generations (which still allows you to use them), making it easier than ever before if users already have an i9 or even an i7 build setup.
Improved Efficiency
Intel’s 13th Generation processors offer absolute gains in computing efficiency compared to previous generations.
This is mainly thanks to the new Thread Director system, which is designed to optimize workload allocation and multitasking across cores.
By identifying processor threads that require heavier processing loads, Thread Director empowers users with increased performance and lower power consumption for their desktops or laptops.
The process further benefits from upgraded classifiers featuring cutting-edge machine learning algorithms enabling efficient decisions when tasking CPUs cores.
As a result, these systems can dramatically cut power requirements while delivering greater performance with less effort and strain on the overall system.
Enhanced Graphics Capabilities
Intel’s 13th Gen CPUs offer significantly improved graphics capabilities for gamers and professionals who use applications that require high graphic performance.
These improvements are enabled by leveraging advanced processors with more powerful integrated GPUs, enabling higher resolutions at faster speeds.
These gains in graphical performance can also improve productivity as well as playability—the 11th gen chips support DirectX 12 Ultimate API which provides hardware-accelerated ray tracing capabilities along with shader cache optimization.
This will result in smoother gaming experiences, especially during fast-paced scenes or sequences requiring rigs featuring complex sets of textures and image effects.
Comparison With Previous Generations Of Intel Processors
| Generation | Performance Improvements | Power Consumption |
| 13th Gen | – Up to 15% increase in single-threaded performance– Up to 41% increase in multi-threaded performance– Better support for DDR5 RAMs and PCIe 5.0 storage devices- 12% to 15% performance increase with 700-series motherboards | Improved efficiency due to workload allocation and core architecture |
| 12th Gen | – Moderate performance increase from 11th Gen- Support for DDR4 RAMs and PCIe 4.0 storage devices- Improved performance in some applications, but lesser than 13th Gen | Higher power consumption compared to 13th Gen |
| 11th Gen | – Lower single-threaded and multi-threaded performance compared to newer generations- Limited performance improvements over 10th Gen | Less efficient power consumption compared to newer generations |
The notable performance improvements in the 13th Gen processors are particularly beneficial for applications requiring a heavy workload across multiple cores, such as Adobe Premiere.
Upgrading to the 13th Gen CPU does not require replacing the motherboard, PSU, or RAM sticks (unless you want DDR5 RAMs), making it a more affordable investment compared to the previous generations.
Intel’s support for both DDR4 and DDR5 RAMs demonstrates its commitment to advancing technology, and the combination of the CPU and motherboard provides optimal connectivity and improved efficiency.
Compatibility With Operating Systems And Applications
Intel’s 13th Gen CPUs are compatible with all Windows 10 / Windows 11 64-bit versions, as well as the Linux operating system.
Assessing Compatibility Issues With Existing Systems And Software
When upgrading to Intel’s 13th Generation Processors, it is important to look at compatibility issues between system hardware and software.
This includes assessing the requirements for supporting motherboards, RAM sticks, and other peripherals that must be compatible with the new processor.
To ensure a successful upgrade, consider the following:
∙€Operating System Compatibility: Will your current operating system support Intel’s 13th Gen CPUs? Some platforms may require additional updates or patches to accommodate this generation of processors.
∙€Application Compatibility: Depending on which applications you plan on using, make sure they are compatible with these latest processors before upgrading. Older programs may be less effective while newer ones may unlock even more performance than their predecessors due to various improvements such as multi-threading support or enhanced graphics capabilities offered by Intel’s 13th Gen CPUs.
∙€Hardware Requirements: Motherboards based on 600 series chipsets can take advantage of Intel’s improved performance but if you’re looking for an even bigger boost then opt for models based on 700 series chipsets instead – these offer substantially better results in terms of benchmark tests and gaming scenarios alike thanks to improved connectivity features (e.g., higher PCIe storage capabilities).
Conclusion
Upgrading to Intel’s 13th Generation Processors offers a significant performance boost, increased efficiency, and enhanced graphics capabilities.
Single-threaded applications can experience up to 15% faster speeds while multitasking scenarios could benefit from up to 41 % improvements in performance when compared with the 12th Gen Processors.